- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录3882 > PIC16F87T-E/ML (Microchip Technology)IC MCU FLASH 4KX14 EEPROM 28QFN
133
8008H–AVR–04/11
ATtiny48/88
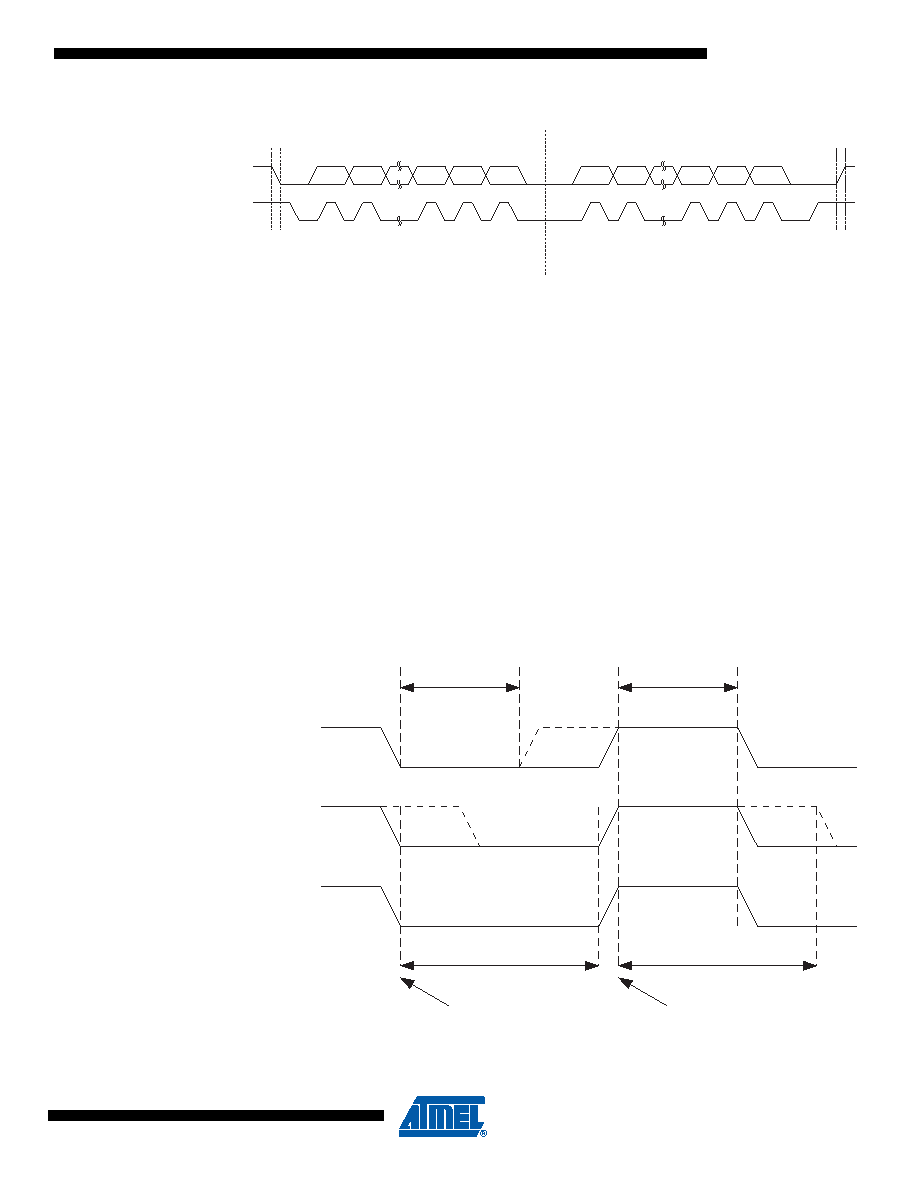
Figure 15-6. Typical Data Transmission
15.5
Multi-master Bus Systems, Arbitration and Synchronization
The TWI protocol allows bus systems with several masters. Special concerns have been taken
in order to ensure that transmissions will proceed as normal, even if two or more masters initiate
a transmission at the same time. Two problems arise in multi-master systems:
An algorithm must be implemented allowing only one of the masters to complete the
transmission. All other masters should cease transmission when they discover that they have
lost the selection process. This selection process is called arbitration. When a contending
master discovers that it has lost the arbitration process, it should immediately switch to Slave
mode to check whether it is being addressed by the winning master. The fact that multiple
masters have started transmission at the same time should not be detectable to the slaves,
i.e. the data being transferred on the bus must not be corrupted.
Different masters may use different SCL frequencies. A scheme must be devised to
synchronize the serial clocks from all masters, in order to let the transmission proceed in a
lockstep fashion. This will facilitate the arbitration process.
Figure 15-7. SCL Synchronization Between Multiple Masters
12
7
8
9
Data Byte
Data MSB
Data LSB
ACK
SDA
SCL
START
12
789
Addr MSB
Addr LSB
R/W
ACK
SLA+R/W
STOP
TA
low
TA
high
SCL from
Master A
SCL from
Master B
SCL Bus
Line
TB
low
TB
high
Masters Start
Counting Low Period
Masters Start
Counting High Period
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
PIC16F87-E/ML
IC MCU FLASH 4KX14 EEPROM 28QFN
PIC18LF4320-I/ML
IC MCU FLASH 4KX16 EEPROM 44QFN
PIC16F77T-I/PTG
IC MCU FLASH 8KX14 W/AD 44TQFP
PIC16LF1933-I/SO
IC PIC MCU FLASH 4K 28-SOIC
PIC16C54C-20I/SO
IC MCU OTP 512X12 18SOIC
PIC16LF726-I/SO
IC PIC MCU FLASH 8K 1.8V 28-SOIC
PIC12CE673-10/P
IC MCU OTP 1KX14 A/D&EE 8DIP
PIC16F726-I/SO
IC PIC MCU FLASH 8KX14 28-SOIC
相关代理商/技术参数
PIC16F87T-E/SO
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 20MHz 4K Flash RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC16F87T-E/SS
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 20MHz 4K Flash RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC16F87T-I/ML
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 7KB 368 RAM 16 I/O RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC16F87T-I/SO
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 7KB 368 RAM 16 I/O RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC16F87T-I/SS
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 7KB 368 RAM 16 I/O RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC16F882-E/ML
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 3.5KB Enh FLSH 128 RAM RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC16F882-E/SO
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 3.5KB Enh FLSH 128 RAM RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC16F882-E/SP
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 3.5KB Enh FLSH 128 RAM RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT